Question 1:
What is the meaning of elasticity?
Answer:
Elasticity is the property of material that enables an object to return to its original shape and size when the force applied on it is removed.
What is the meaning of elasticity?
Answer:
Elasticity is the property of material that enables an object to return to its original shape and size when the force applied on it is removed.
Question 2:
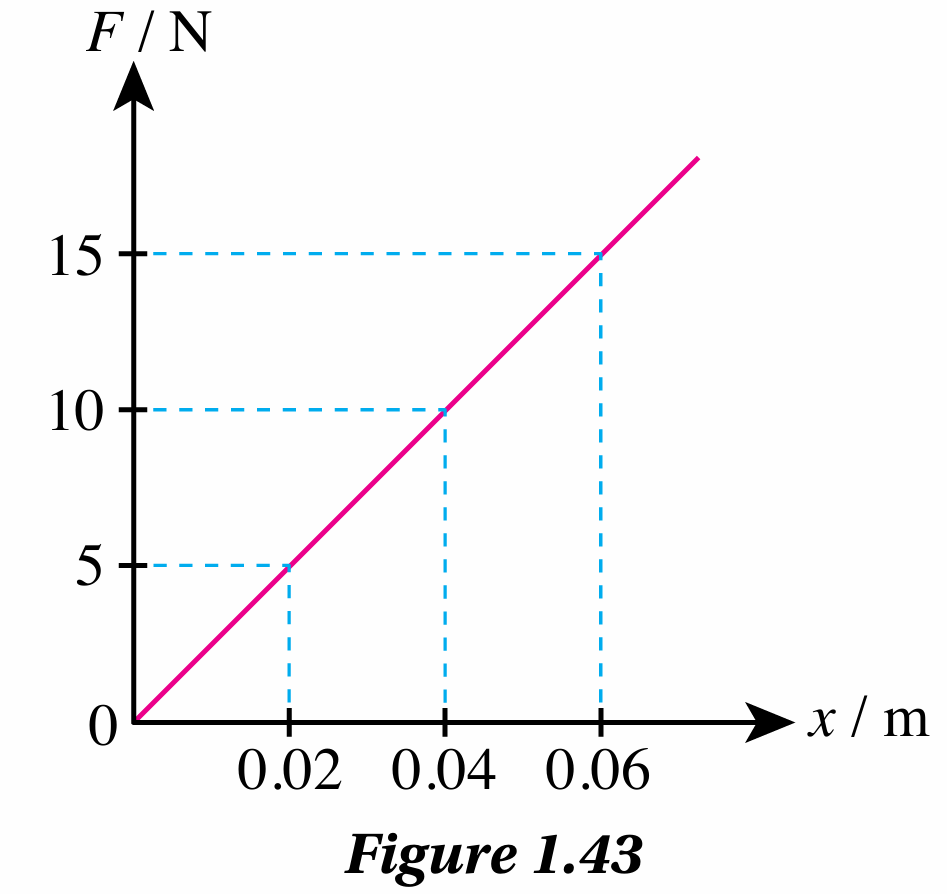
Figure 1.43 shows the graph of force, F against extension, x for a spring.
(a) State Hooke’s law.
(b) Does the spring obey Hooke’s law?
(c) Calculate the spring constant.
(d) What is the elastic potential energy in the spring when stretched to an extension of 0.04 m?
Answer:
(a)
Keywords:
– extension of a spring
– directly proportional
– force applied on the spring
– elastic limit not exceeded
Hooke’s law states that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied on the spring provided the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded.
(b)
Yes, the spring obeys Hooke’s law because the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
(A graph of a straight line that pass through the origin, indicates that the quantity of y-axis (Force, F) is directly proportional to the quantity of the x-axis (Extension, x).)
(c)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Spring constant, } k \\ & =\text { Gradient of the graph } F \text { against } x \\ & =\frac{15}{0.06} \\ & =250 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{-1} \end{aligned} $$
(d)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Elastic potential energy }=\text { Area below the graph } \\ & =\frac{1}{2} \times 0.04 \times 10 \\ & =0.2 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned} $$

Figure 1.43 shows the graph of force, F against extension, x for a spring.
(a) State Hooke’s law.
(b) Does the spring obey Hooke’s law?
(c) Calculate the spring constant.
(d) What is the elastic potential energy in the spring when stretched to an extension of 0.04 m?
Answer:
(a)
Keywords:
– extension of a spring
– directly proportional
– force applied on the spring
– elastic limit not exceeded
Hooke’s law states that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied on the spring provided the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded.
(b)
Yes, the spring obeys Hooke’s law because the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
(A graph of a straight line that pass through the origin, indicates that the quantity of y-axis (Force, F) is directly proportional to the quantity of the x-axis (Extension, x).)
(c)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Spring constant, } k \\ & =\text { Gradient of the graph } F \text { against } x \\ & =\frac{15}{0.06} \\ & =250 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{-1} \end{aligned} $$
(d)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Elastic potential energy }=\text { Area below the graph } \\ & =\frac{1}{2} \times 0.04 \times 10 \\ & =0.2 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned} $$
