In a Displacement-Time Graph, the gradient of the graph is equal to the velocity of motion.
Analysing Displacement – Time Graph
- When analysing the displacement-time graph, always remember that the gradient of the graph represents the velocity of the graph.
- Therefore, if the gradient of the graph is positive, the velocity is positive, and if the gradient of the graph is negative, the velocity is negative.
- A negative velocity indicates that the object moves in the opposite direction.
- The table below shows the displacement-time graph of various motion.
Velocity = 0
This is a horizontal straight line, hence the gradient = 0.
Therefore, the velocity = gradient of the graph = 0, which means the object is stationary (does not move).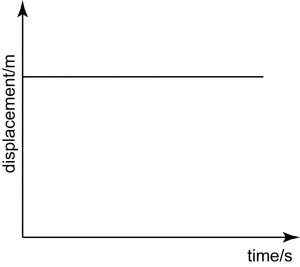
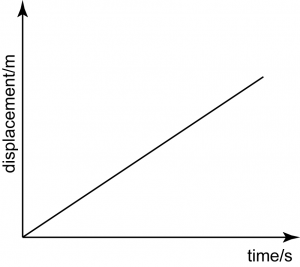
Uniform Velocity
The graph is a non-horizontal straight line, hence the gradient is not equal to 0. For a straight line, the gradient is constant,
hence, the velocity of the moving object is uniform.
Negative Uniform Velocity
The graph is a non-horizontal straight line, with a negative gradient. For the straight line, the gradient must be constant. The negative value of gradient indicates that the object moves in the opposite direction.
Therefore, this graph represents a motion with uniform velocity in opposite direction.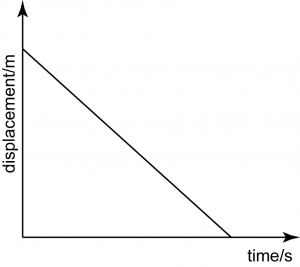
Increasing Velocity
The graph is a curve, shows that the gradient is not constant. The gradient increases over time, indicates that the velocity increases over time.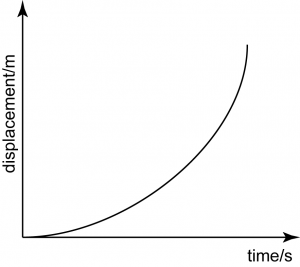
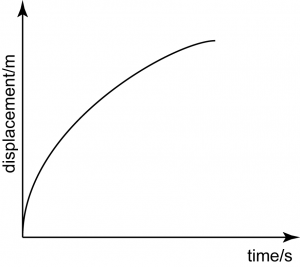
Decreasing Acceleration
The gradient decreases over time shows that the velocity of the moving object decreases over time.