Boyle’s law
Boyle’s law states that the pressure of a gas with constant mass is inversely proportional to its volume provided the temperature of the gas is kept constant.

Formula:
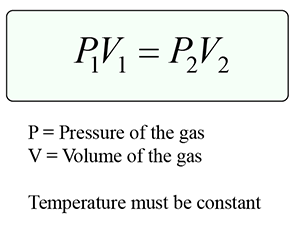
Explanation
- When the volume of gas decreases, the number of gas particles per unit volume increases.
- As a result, the frequency of collision between the air particles and the wall of the container increases.
- As such, the pressure of the gas increases.
Graph
- In the graphs above, the first graph shows that P is inversely proportional to V.
- The second graph shows that P is directly proportional to 1/V.
- The third and the forth graphs shows that PV is always constant for all value of V and P.