Question 4:
(a) Define specific latent heat.
(b) Th e mass of a melting ice cube reduces by 0.68 kg. What is the amount of heat absorbed from the surrounding by the ice cube?
[Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.34 × 105 J kg–1]
Answer:
(a) Specific latent heat is the quantity of heat absorbed or released by 1 kg of a substance during a change in its phase without any change in its temperature.
(b)
\begin{aligned} Q & =m l \\ & =0.68 \times\left(3.34 \times 10^5\right) \\ & =2.27 \times 10^5 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned}
(a) Define specific latent heat.
(b) Th e mass of a melting ice cube reduces by 0.68 kg. What is the amount of heat absorbed from the surrounding by the ice cube?
[Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.34 × 105 J kg–1]
Answer:
(a) Specific latent heat is the quantity of heat absorbed or released by 1 kg of a substance during a change in its phase without any change in its temperature.
(b)
\begin{aligned} Q & =m l \\ & =0.68 \times\left(3.34 \times 10^5\right) \\ & =2.27 \times 10^5 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned}
Question 5:
(a) What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporisation?
(b) Figure 1 shows the graph of mass of water, m against time, t when water in a beaker is heated by a 1 800 W electric heater. At time t = 360 s, the water starts to boil.
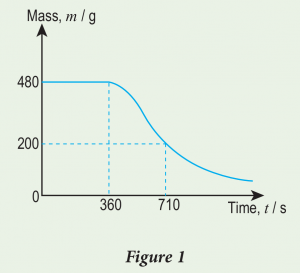
Calculate:
(i) mass of water that becomes steam from t = 360 s until t = 710 s.
(ii) specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
Answer:
(a) Specific latent heat of vaporisation, lv of a substance is the quantity of heat absorbed by 1 kg of the substance when boiling or the quantity of heat released by 1 kg of the substance when condensing without any change in its temperature.
(b)(i)
From the graph, mass of water, \begin{aligned} m & =480-200 \\ & =280 \mathrm{~g} \\ & =0.28 \mathrm{~kg}\end{aligned}
(b)(ii)
\begin{aligned} & Q=m l \\ & P t=m l \\ & 1800 \times(710-360)=0.28 \times l \\ & l=\frac{1800 \times 350}{0.28} \\ & l=2.25 \times 10^6 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1} \end{aligned}
(a) What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporisation?
(b) Figure 1 shows the graph of mass of water, m against time, t when water in a beaker is heated by a 1 800 W electric heater. At time t = 360 s, the water starts to boil.

Calculate:
(i) mass of water that becomes steam from t = 360 s until t = 710 s.
(ii) specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
Answer:
(a) Specific latent heat of vaporisation, lv of a substance is the quantity of heat absorbed by 1 kg of the substance when boiling or the quantity of heat released by 1 kg of the substance when condensing without any change in its temperature.
(b)(i)
From the graph, mass of water, \begin{aligned} m & =480-200 \\ & =280 \mathrm{~g} \\ & =0.28 \mathrm{~kg}\end{aligned}
(b)(ii)
\begin{aligned} & Q=m l \\ & P t=m l \\ & 1800 \times(710-360)=0.28 \times l \\ & l=\frac{1800 \times 350}{0.28} \\ & l=2.25 \times 10^6 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1} \end{aligned}
Question 6:
Sebentuk cincin emas berjisim 5.5 g mengalami peningkatan suhu dari 36°C hingga 39°C. Berapakah tenaga haba yang telah diserap oleh cincin tersebut?
[Diberi nilai muatan haba tentu emas ialah 300 J kg–1 °C–1]
Answer:
\begin{aligned} m & =5.5 \mathrm{~g} \\ & =0.0055 \mathrm{~kg} \text { or } 5.5 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~kg}\end{aligned} \begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ & =\left(5.5 \times 10^{-3}\right)(300)(3) \\ & =4.95 \mathrm{~J}\end{aligned}
Sebentuk cincin emas berjisim 5.5 g mengalami peningkatan suhu dari 36°C hingga 39°C. Berapakah tenaga haba yang telah diserap oleh cincin tersebut?
[Diberi nilai muatan haba tentu emas ialah 300 J kg–1 °C–1]
Answer:
\begin{aligned} m & =5.5 \mathrm{~g} \\ & =0.0055 \mathrm{~kg} \text { or } 5.5 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~kg}\end{aligned} \begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ & =\left(5.5 \times 10^{-3}\right)(300)(3) \\ & =4.95 \mathrm{~J}\end{aligned}
