Question 3:
Figure 2 shows a full-wave rectification kit connected to an alternating current power supply and a cathode ray oscilloscope.
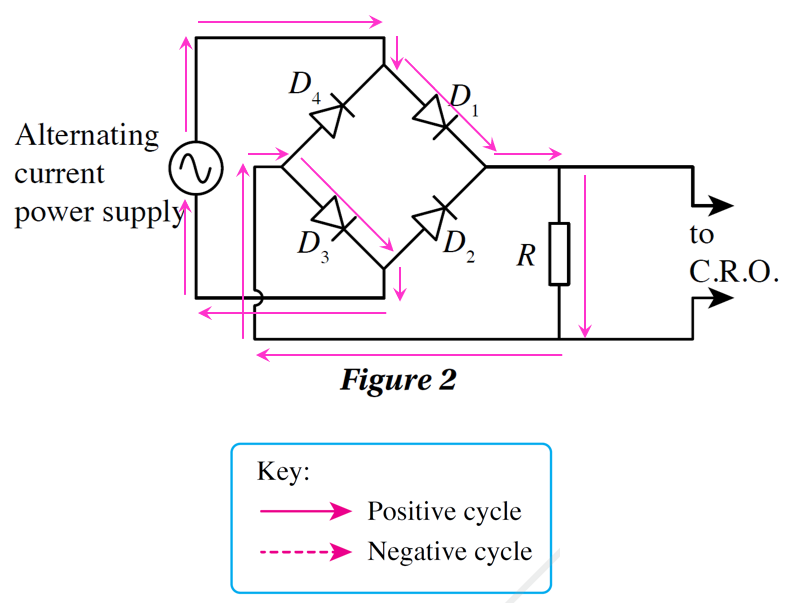
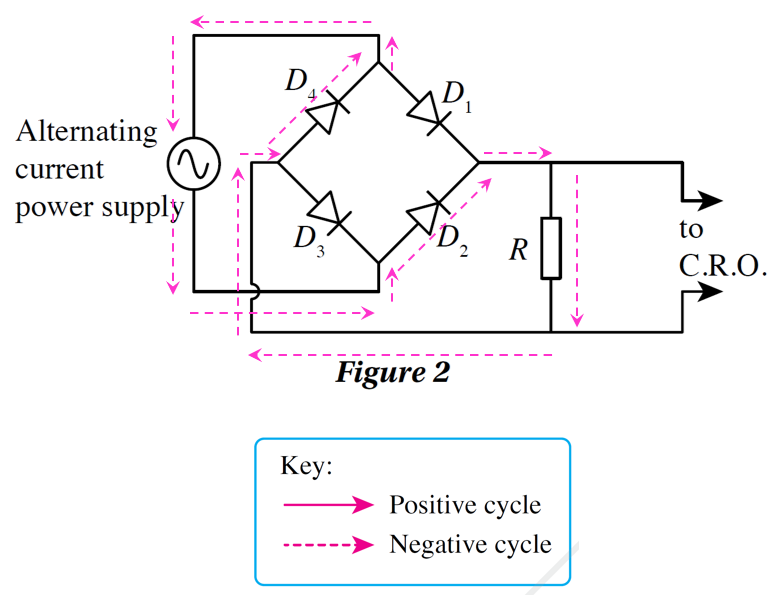
(a) draw arrows to show the flow of current through the diode during the positive half cycle and the negative half cycle.
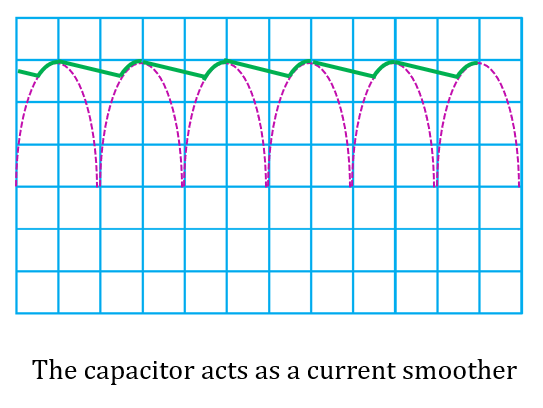
(b) Sketch what is displayed on the cathode ray oscilloscope screen if a capacitor is connected parallel to the resistor, R. What is the role of the capacitor?
(c) What will happen to the output current if the connection to diode, D1 is reversed?
Answer:
(a)
(b)
(c) Half-wave rectification will occur
Figure 2 shows a full-wave rectification kit connected to an alternating current power supply and a cathode ray oscilloscope.

(a) draw arrows to show the flow of current through the diode during the positive half cycle and the negative half cycle.
(b) Sketch what is displayed on the cathode ray oscilloscope screen if a capacitor is connected parallel to the resistor, R. What is the role of the capacitor?
(c) What will happen to the output current if the connection to diode, D1 is reversed?
Answer:
(a)


(b)

(c) Half-wave rectification will occur
Question 4:
Table 1 shows the main components that are required for a transistor to function as an automatic light-controlled switch.
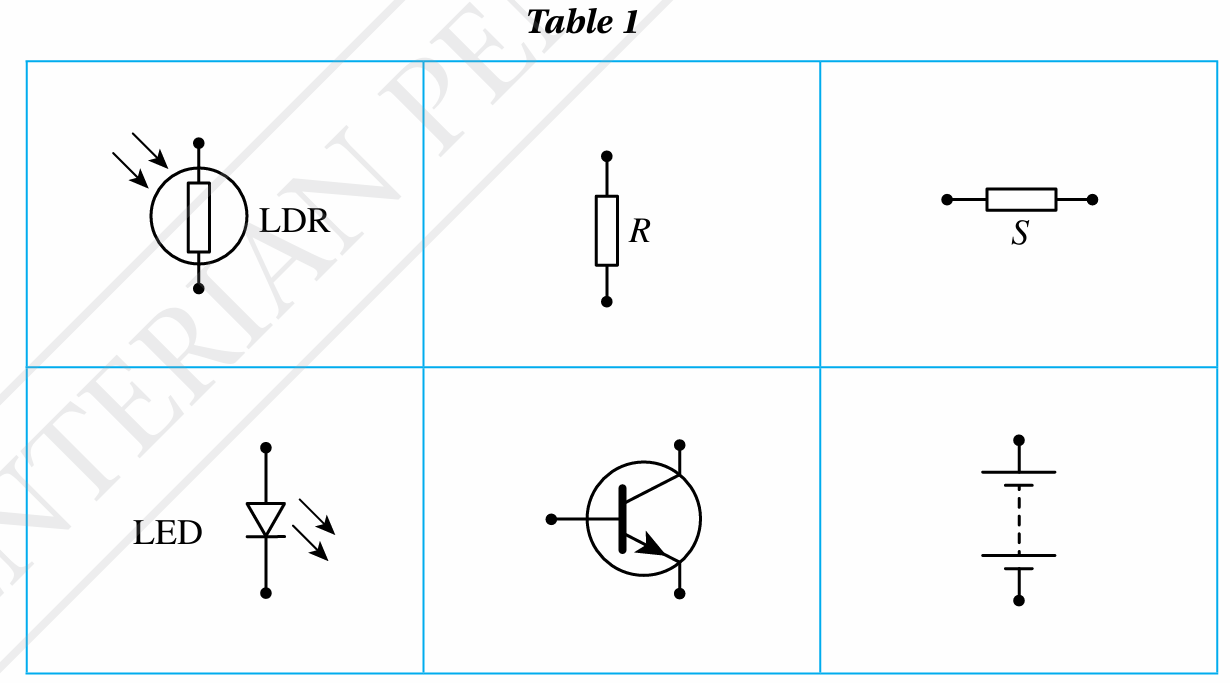
(a) draw an automatic switch transistor circuit using the components provided in the table above.
(b) Discuss whether the LED is lighted when the LDR is under bright conditions.
(c) State the modification of the automatic switch transistor circuit to an automatic temperature-controlled alarm circuit so that the alarm will ring when its surrounding temperature becomes very high.
Answer:
(a)
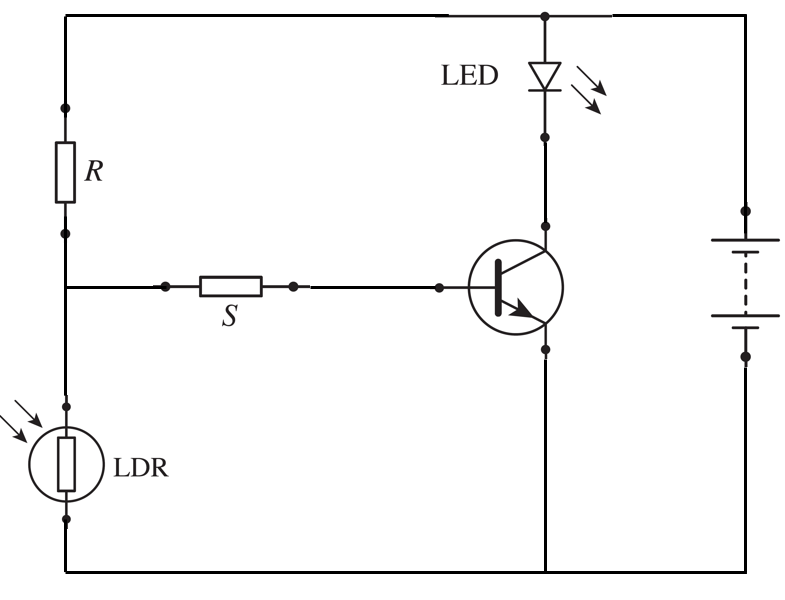
(b) Under bright conditions, LDR resistance becomes low.
Therefore, the voltage across LDR decreases but the voltage across R is increased. The IB is low, and the transistor is turned off. The IC will be low, and the LED will not light up.
(c) Replace LED with an alarm, replace resistor with a thermistor and the LDR with a resistor.
Table 1 shows the main components that are required for a transistor to function as an automatic light-controlled switch.

(a) draw an automatic switch transistor circuit using the components provided in the table above.
(b) Discuss whether the LED is lighted when the LDR is under bright conditions.
(c) State the modification of the automatic switch transistor circuit to an automatic temperature-controlled alarm circuit so that the alarm will ring when its surrounding temperature becomes very high.
Answer:
(a)

(b) Under bright conditions, LDR resistance becomes low.
Therefore, the voltage across LDR decreases but the voltage across R is increased. The IB is low, and the transistor is turned off. The IC will be low, and the LED will not light up.
(c) Replace LED with an alarm, replace resistor with a thermistor and the LDR with a resistor.
