Question 11:
An electric kettle is filled with 500 g of water at 30°C. The power of the heating element of the kettle is 0.8 kW. Assume that all heat from the heating element is transferred to the water.
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4 200 J kg–1 °C–1.]
(a) Calculate:
(i) heat energy needed to increase the temperature of the water to 100°C.
(ii) time taken by the kettle to heat water to a temperature of 100°C.
(b) Why is the handle of the kettle made of plastic?
(c) Why is the heating element of the kettle made of metal?
(d) The heating element of the kettle is located at the base of the kettle. Explain why.
Answer:
\begin{aligned} & m=500 \mathrm{~g}=0.5 \mathrm{~kg} \\ & P=0.8 \mathrm{~kW}=800 \mathrm{~W} \end{aligned}
(a)(i)
\begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ & =(0.5)(4200)(100-30) \\ & =147000 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned}
(a)(ii)
\begin{aligned} P t & =Q \\ t & =\frac{Q}{P} \\ & =\frac{147000}{800} \\ & =183.75 \mathrm{~s} \end{aligned}
(b)
Plastics have high specific heat capacities and are heat insulators.
(c)
Metals have low specific heat capacities and are good heat conductors.
(d)
Water rises when heated and cold-water sinks through convection. So, all the water is heated. Therefore, the heating element of a kettle is fitted at the base of the kettle.
An electric kettle is filled with 500 g of water at 30°C. The power of the heating element of the kettle is 0.8 kW. Assume that all heat from the heating element is transferred to the water.
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4 200 J kg–1 °C–1.]
(a) Calculate:
(i) heat energy needed to increase the temperature of the water to 100°C.
(ii) time taken by the kettle to heat water to a temperature of 100°C.
(b) Why is the handle of the kettle made of plastic?
(c) Why is the heating element of the kettle made of metal?
(d) The heating element of the kettle is located at the base of the kettle. Explain why.
Answer:
\begin{aligned} & m=500 \mathrm{~g}=0.5 \mathrm{~kg} \\ & P=0.8 \mathrm{~kW}=800 \mathrm{~W} \end{aligned}
(a)(i)
\begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ & =(0.5)(4200)(100-30) \\ & =147000 \mathrm{~J} \end{aligned}
(a)(ii)
\begin{aligned} P t & =Q \\ t & =\frac{Q}{P} \\ & =\frac{147000}{800} \\ & =183.75 \mathrm{~s} \end{aligned}
(b)
Plastics have high specific heat capacities and are heat insulators.
(c)
Metals have low specific heat capacities and are good heat conductors.
(d)
Water rises when heated and cold-water sinks through convection. So, all the water is heated. Therefore, the heating element of a kettle is fitted at the base of the kettle.
Question 12:
A substance has a mass of 250 g. Th e substance loses 5 625 J of heat when cooled. There is a 25°C drop in temperature.
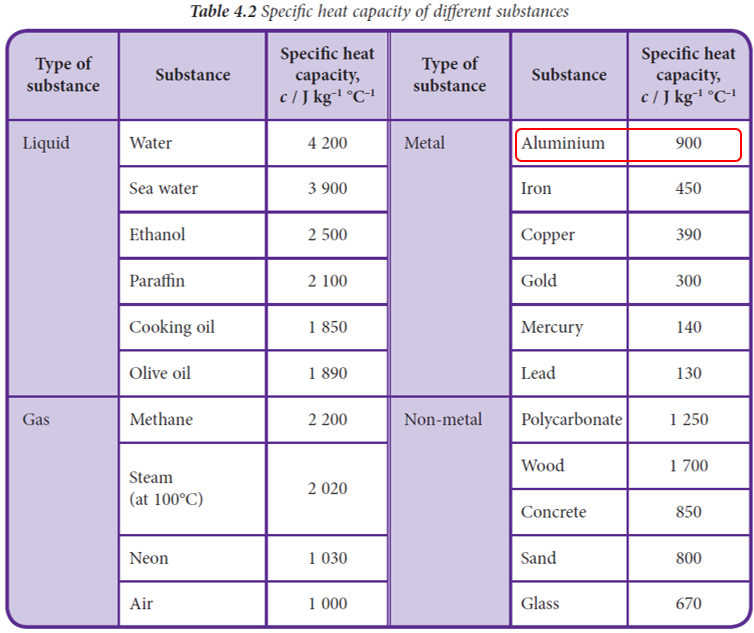
(a) Calculate the specific heat capacity of the substance. Identify the substance based on Table 4.2 on page 128.
(b) Explain the use of the substance based on its specific heat capacity.
Answer:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ c & =\frac{Q}{m \theta} \\ & =\frac{5625}{(0.25)(25)} \\ & =900 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \end{aligned} $$ Referring to Table 4.2, the said substance is aluminium.
(b)
Aluminium has a low specific heat capacity and is a good conductor of heat. Therefore, aluminium is suitable for making cooking utensils.
A substance has a mass of 250 g. Th e substance loses 5 625 J of heat when cooled. There is a 25°C drop in temperature.
(a) Calculate the specific heat capacity of the substance. Identify the substance based on Table 4.2 on page 128.
(b) Explain the use of the substance based on its specific heat capacity.
Answer:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} Q & =m c \theta \\ c & =\frac{Q}{m \theta} \\ & =\frac{5625}{(0.25)(25)} \\ & =900 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \end{aligned} $$ Referring to Table 4.2, the said substance is aluminium.

(b)
Aluminium has a low specific heat capacity and is a good conductor of heat. Therefore, aluminium is suitable for making cooking utensils.
