Question 5:
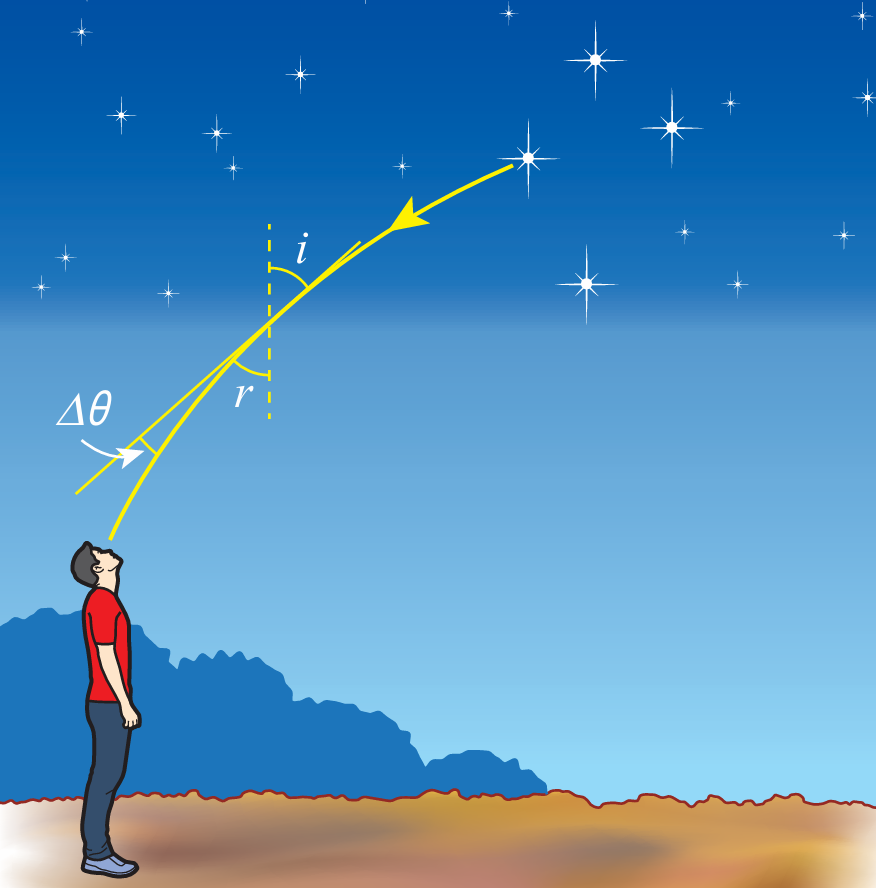
When light from a star travels into the Earth’s atmosphere, its direction of travel will change. This situation is shown in Figure 5. The change of direction is represented by the angle Δθ = i − r.
(a) Speed of light in air is 299 910 km s−1 and speed of light in vacuum is 3.00 × 108 m s−1.
(i) Calculate the refractive index of air.
(ii) Explain the value of refractive index obtained.
(b) Value of Δθ on a hot night is different from that on a cold night. State a logical reason for the difference.
(c) Rajiv returns from school in a school van on a hot and bright day. Rajiv can see a puddle of water on the surface of the road ahead. When the van reaches the location of the puddle of water, Rajiv discovers that the puddle of water does not actually exist. Explain this phenomenon.
Answer:
(a)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} n & =\frac{c}{v} \\ n & =\frac{3.0 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}{2.9991 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}} \\ & =1.0003 \end{aligned} $$
(a)(ii) The value of the refractive index of air is almost equal to 1 , that is the speeds of light in air and in vacuum are almost the same.
(b) The value Δθ on a hot night is different from that on a cold night because the optical density of air depends on temperature.
(c)
Layers of air above the road have different optical density.
The layer of air just above the road surface is hotter than the upper layers.
The layer of hot air has smaller optical density than cold air.
Light which travels from the upper layer to the lower layer is refracted away from the normal repeatedly.
When the angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle of air, total internal reflection occurs.
Reflected light rays are then refracted towards the normal and reach Rajiv’s eyes.
Rajiv will see the image of clouds as a puddle of water on the road surface.

When light from a star travels into the Earth’s atmosphere, its direction of travel will change. This situation is shown in Figure 5. The change of direction is represented by the angle Δθ = i − r.
(a) Speed of light in air is 299 910 km s−1 and speed of light in vacuum is 3.00 × 108 m s−1.
(i) Calculate the refractive index of air.
(ii) Explain the value of refractive index obtained.
(b) Value of Δθ on a hot night is different from that on a cold night. State a logical reason for the difference.
(c) Rajiv returns from school in a school van on a hot and bright day. Rajiv can see a puddle of water on the surface of the road ahead. When the van reaches the location of the puddle of water, Rajiv discovers that the puddle of water does not actually exist. Explain this phenomenon.
Answer:
(a)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} n & =\frac{c}{v} \\ n & =\frac{3.0 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}{2.9991 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}} \\ & =1.0003 \end{aligned} $$
(a)(ii) The value of the refractive index of air is almost equal to 1 , that is the speeds of light in air and in vacuum are almost the same.
(b) The value Δθ on a hot night is different from that on a cold night because the optical density of air depends on temperature.
(c)
Layers of air above the road have different optical density.
The layer of air just above the road surface is hotter than the upper layers.
The layer of hot air has smaller optical density than cold air.
Light which travels from the upper layer to the lower layer is refracted away from the normal repeatedly.
When the angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle of air, total internal reflection occurs.
Reflected light rays are then refracted towards the normal and reach Rajiv’s eyes.
Rajiv will see the image of clouds as a puddle of water on the road surface.
Question 6:
Figure 6 shows an object and its virtual image formed by a convex lens.
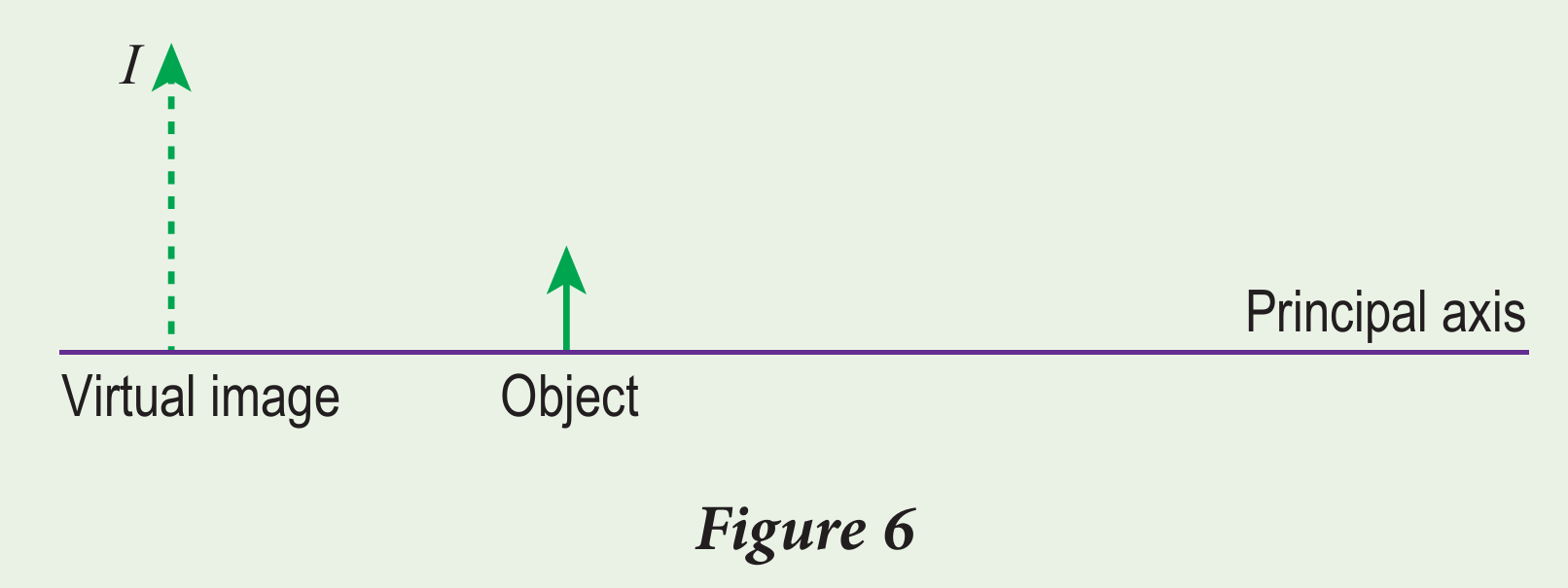
(a) One of the characteristics of image I in Figure 6 is that it is virtual. State the other characteristics of image I.
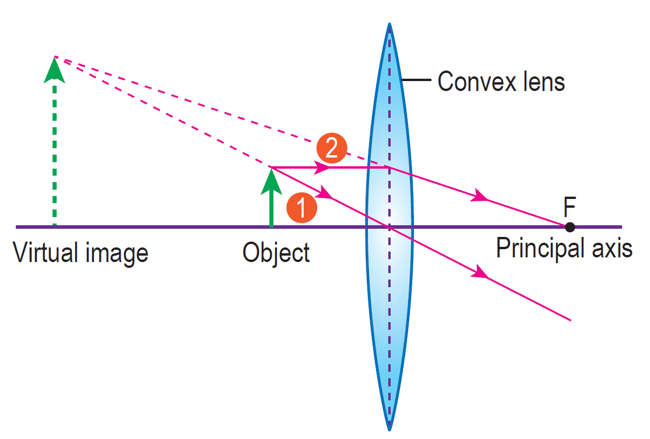
(b) Complete the ray diagram in Figure 6 and determine the position of the lens and focal point of the lens. Mark the position of the focal point of the lens with, F.
(c) If the object is slowly moved away from the lens, state two changes that might happen to the image without drawing a ray diagram.
Answer:
(a) Upright and magnified
(b)
(c) The image will turn real, inverted, diminished and formed on the opposite side of the lens from the object.
Figure 6 shows an object and its virtual image formed by a convex lens.

(a) One of the characteristics of image I in Figure 6 is that it is virtual. State the other characteristics of image I.
(b) Complete the ray diagram in Figure 6 and determine the position of the lens and focal point of the lens. Mark the position of the focal point of the lens with, F.
(c) If the object is slowly moved away from the lens, state two changes that might happen to the image without drawing a ray diagram.
Answer:
(a) Upright and magnified
(b)

(c) The image will turn real, inverted, diminished and formed on the opposite side of the lens from the object.
