Question 1:
Complete the radioactive decay equation. Identify A, B and C.
(a) $$ { }_{88}^{228} \mathrm{Ra} \rightarrow A+{ }_{-1}^0 e $$
(b) \begin{equation} { }_{84}^{209} \mathrm{Po} \rightarrow{ }_{82}^{205} \mathrm{~Pb}+B \end{equation}
(c) \begin{equation} C \rightarrow{ }_1^1 p+{ }_{-1}^0 e \end{equation}
Answer:
(a)
The general equation for β-decay is
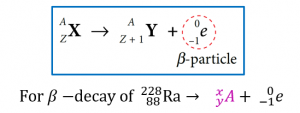
$$ \begin{aligned} 228 & =x+0 \\ x & =228 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 88 & =y+(-1) \\ y & =88+1 \\ y & =89 \end{aligned} $$
$$ A={ }_{89}^{228} \mathrm{Ac} $$
(b)
The general equation for α-decay is
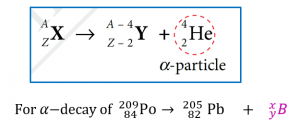
$$ \begin{aligned} 209 & =205+x \\ x & =209-205 \\ x & =4 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 84 & =82+y \\ y & =84-82 \\ y & =2 \end{aligned} $$
$$ B={ }_2^4 \mathrm{He} $$
(c)
During beta decay, a neutron in an unstable nucleus decomposes into one proton and one electron
$$ \begin{aligned} & { }_0^1 n \rightarrow{ }_1^1 p+{ }_{-1}^0 e \\ & C={ }_0^1 n \end{aligned} $$
Complete the radioactive decay equation. Identify A, B and C.
(a) $$ { }_{88}^{228} \mathrm{Ra} \rightarrow A+{ }_{-1}^0 e $$
(b) \begin{equation} { }_{84}^{209} \mathrm{Po} \rightarrow{ }_{82}^{205} \mathrm{~Pb}+B \end{equation}
(c) \begin{equation} C \rightarrow{ }_1^1 p+{ }_{-1}^0 e \end{equation}
Answer:
(a)
The general equation for β-decay is

$$ \begin{aligned} 228 & =x+0 \\ x & =228 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 88 & =y+(-1) \\ y & =88+1 \\ y & =89 \end{aligned} $$
$$ A={ }_{89}^{228} \mathrm{Ac} $$

(b)
The general equation for α-decay is
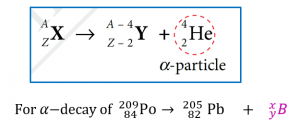
$$ \begin{aligned} 209 & =205+x \\ x & =209-205 \\ x & =4 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 84 & =82+y \\ y & =84-82 \\ y & =2 \end{aligned} $$
$$ B={ }_2^4 \mathrm{He} $$
(c)
During beta decay, a neutron in an unstable nucleus decomposes into one proton and one electron
$$ \begin{aligned} & { }_0^1 n \rightarrow{ }_1^1 p+{ }_{-1}^0 e \\ & C={ }_0^1 n \end{aligned} $$
Question 2:
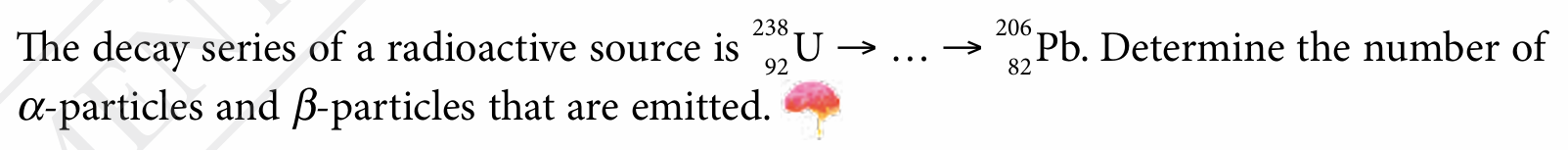
Answer:
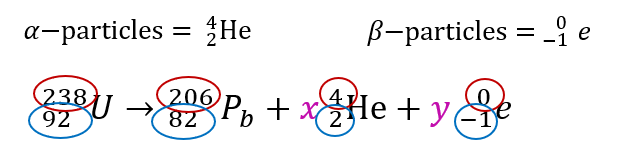
$$ \begin{aligned} 238 & =206+4(x)+0(y) \\ 4 x & =238-206 \\ 4 x & =32 \\ x & =8 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 92 & =82+2(x)-1(y) \\ 92 & =82+2(8)-y \\ y & =82+16-92 \\ y & =6 \end{aligned} $$
The number of particles that are emitted is 8α-particles and 6β-particles.
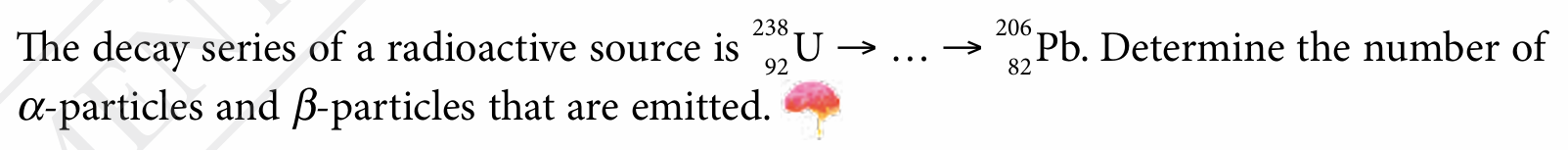
Answer:
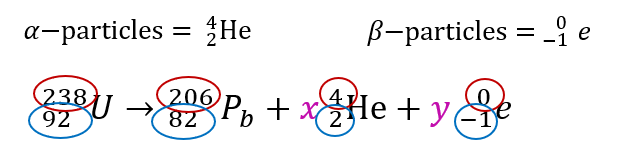
$$ \begin{aligned} 238 & =206+4(x)+0(y) \\ 4 x & =238-206 \\ 4 x & =32 \\ x & =8 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 92 & =82+2(x)-1(y) \\ 92 & =82+2(8)-y \\ y & =82+16-92 \\ y & =6 \end{aligned} $$
The number of particles that are emitted is 8α-particles and 6β-particles.
Question 3:
Table 6.4 shows the record of the activity of a radioactive sample stored in the laboratory.
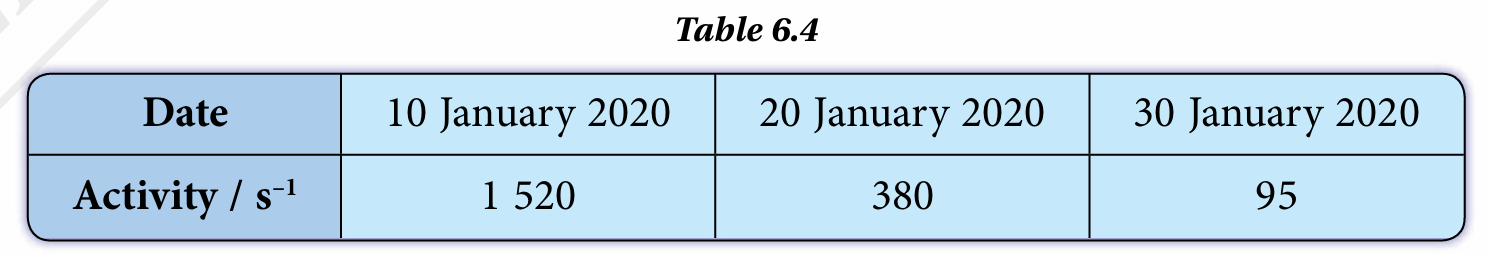
(a) Determine the half-life of the radioactive sample.
(b) Sketch a radioactive decay curve for the sample.
Answer:
(a)

$$ \begin{aligned} N_0 & =1520 \\ N & =95 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} N & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n N_0 \\ 95 & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n 1520 \\ \frac{95}{1520} & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ \frac{1}{16} & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^4 & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ n & =4 \end{aligned} $$
10 Jan -30 Jan, 4 half-lives in 20 days
$$ T_{\frac{1}{2}}=\frac{t}{n} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} T_{\frac{1}{2}} & =\frac{20 \text { days }}{4} \\ & =5 \end{aligned} $$
Therefore, the half-life is 5 days
(b)
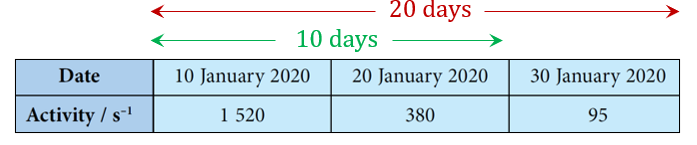
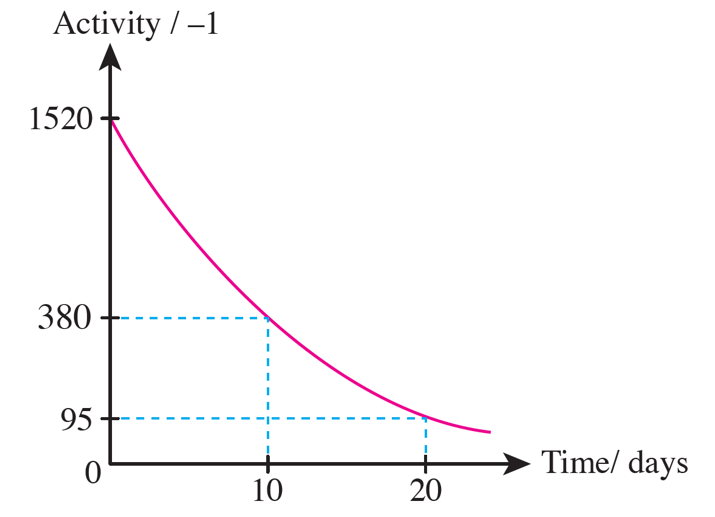
Table 6.4 shows the record of the activity of a radioactive sample stored in the laboratory.

(a) Determine the half-life of the radioactive sample.
(b) Sketch a radioactive decay curve for the sample.
Answer:
(a)

$$ \begin{aligned} N_0 & =1520 \\ N & =95 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} N & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n N_0 \\ 95 & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n 1520 \\ \frac{95}{1520} & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ \frac{1}{16} & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^4 & =\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^n \\ n & =4 \end{aligned} $$
10 Jan -30 Jan, 4 half-lives in 20 days
$$ T_{\frac{1}{2}}=\frac{t}{n} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} T_{\frac{1}{2}} & =\frac{20 \text { days }}{4} \\ & =5 \end{aligned} $$
Therefore, the half-life is 5 days
(b)


