Question 1:
Figure 5.71 shows an electromagnetic spectrum.
 What are waves A, B and C?
What are waves A, B and C?
Answer:
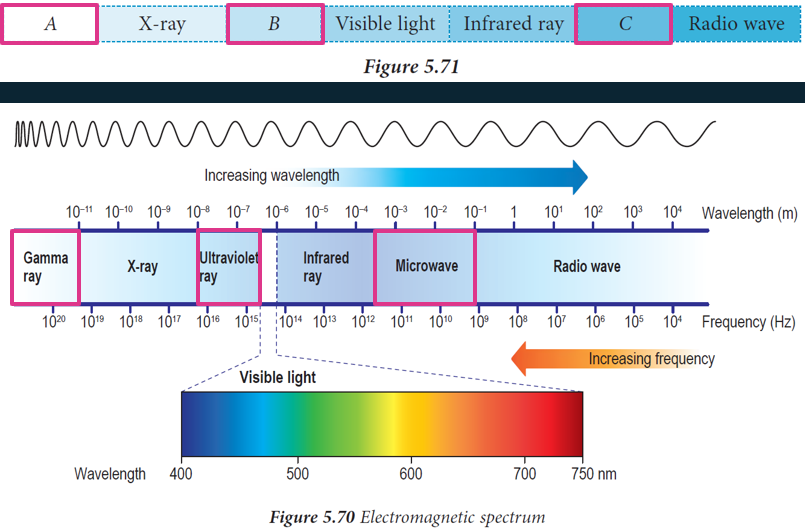
$$ \begin{aligned} & A=\text { Gamma ray } \\ & B=\text { Ultraviolet ray } \\ & C=\text { Microwave } \end{aligned} $$
Figure 5.71 shows an electromagnetic spectrum.
 What are waves A, B and C?
What are waves A, B and C?Answer:

$$ \begin{aligned} & A=\text { Gamma ray } \\ & B=\text { Ultraviolet ray } \\ & C=\text { Microwave } \end{aligned} $$
Question 2:
Arrange the electromagnetic waves below according to the order of increasing frequency.

Answer:
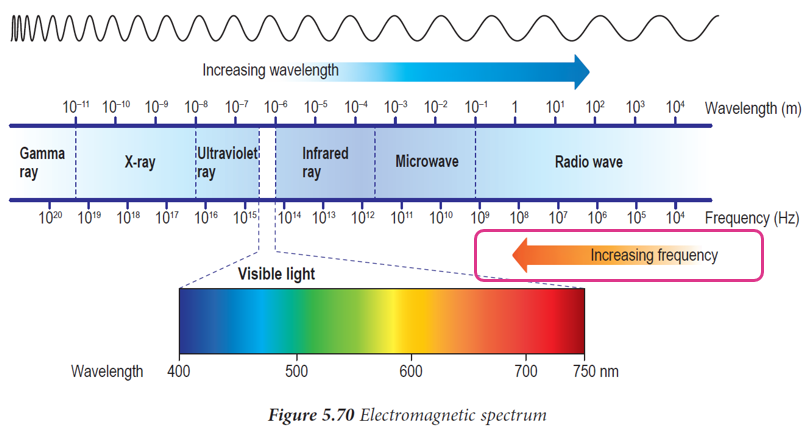

Arrange the electromagnetic waves below according to the order of increasing frequency.

Answer:


Question 3:
In the air, blue light with a wavelength of 420 nm moves at a speed of 3.00 × 108 m s–1. The speed of the blue light reduces to 2.25 × 108 m s–1 when passing through a liquid. What is the wavelength of the blue light in the liquid?
Answer:
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { In the air : } v_1 & =3.00 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1} \\ \lambda_1 & =420 \mathrm{~nm} \\ \text { In liquid: } v_2 & =2.25 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1} \\ \lambda_2 & =? \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} {[2] \div[1]: \frac{2.25 \times 10^8}{3.00 \times 10^8} } & =\frac{\lambda_2}{420} \\ \lambda_2 & =\frac{\left(2.25 \times 10^8\right) \times 420}{3.00 \times 10^8} \\ \lambda_2 & =315 \mathrm{~nm} \end{aligned} $$
In the air, blue light with a wavelength of 420 nm moves at a speed of 3.00 × 108 m s–1. The speed of the blue light reduces to 2.25 × 108 m s–1 when passing through a liquid. What is the wavelength of the blue light in the liquid?
Answer:
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { In the air : } v_1 & =3.00 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1} \\ \lambda_1 & =420 \mathrm{~nm} \\ \text { In liquid: } v_2 & =2.25 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1} \\ \lambda_2 & =? \end{aligned} $$
Frequency in the air = Frequency in the liquid
Using equation, v = fλ
In the air : 3.00 × 108 = f × 420………[1]
In the liquid : 2.25 × 108 = f × λ2………[2]
$$ \begin{aligned} {[2] \div[1]: \frac{2.25 \times 10^8}{3.00 \times 10^8} } & =\frac{\lambda_2}{420} \\ \lambda_2 & =\frac{\left(2.25 \times 10^8\right) \times 420}{3.00 \times 10^8} \\ \lambda_2 & =315 \mathrm{~nm} \end{aligned} $$
