 [This image is original released under GNU Free Documentation license ]
[This image is original released under GNU Free Documentation license ]What is the transformer?
A transformer is a device that is used to raise or lower down the potential difference of an alternating current.
Function:
The function of a transformer is to increase or decrease the potential difference of an alternating current supply.
Structure and Technical Terms
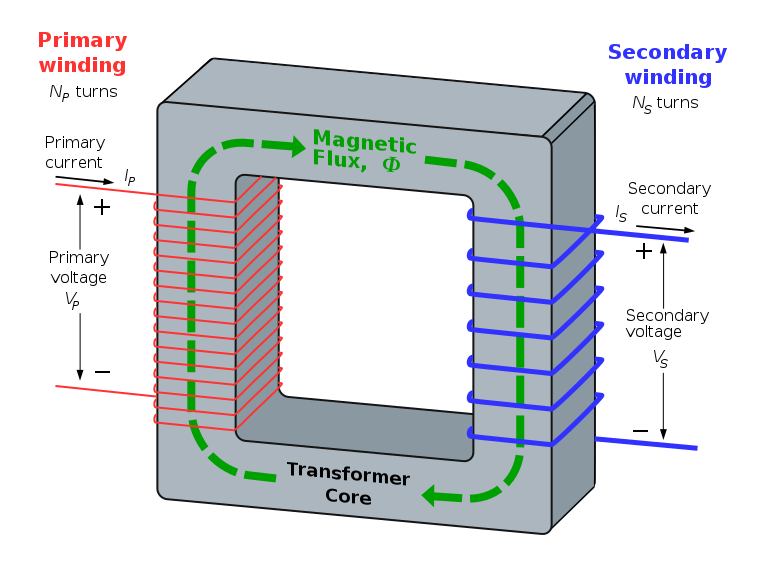
1. A transformer consist of 3 parts, namely
- The primary circuit
- The core
- The secondary Circuit
 [This image is released under the GNU Free Documentation License.]
[This image is released under the GNU Free Documentation License.]Primary Circuit:
The primary circuit is the circuit that connected to the input energy source. The current, potential difference and coil (winding) in the primary circuit are called the primary current (Ip), primary potential difference (Vp) and primary coil respectively.
Core:
The core is the ferromagnetic metal wound by the primary and secondary coil. The function of the core is to transfer the changing magnetic flux from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
The core is the ferromagnetic metal wound by the primary and secondary coil. The function of the core is to transfer the changing magnetic flux from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
Secondary Circuit:
The secondary circuit is the circuit that connected to the output of the transformer. The current, potential difference and coil (winding) in the secondary circuit are called the secondary current (Is), secondary potential difference (Vs) and secondary coil respectively.
The secondary circuit is the circuit that connected to the output of the transformer. The current, potential difference and coil (winding) in the secondary circuit are called the secondary current (Is), secondary potential difference (Vs) and secondary coil respectively.
Working Principle of A Transformer
- A transformer consists of a primary coil and a secondary coil wound on a soft iron core.
- When an alternating current flows in the primary coil, a changing magnetic flux is generated around the primary coil.
- The changing magnetic flux is transferred to the secondary coil through the iron core.
- The changing magnetic flux is cut by the secondary coil, hence induces an e.m.f. in the secondary coil.
- The magnitude of the output voltage can be controlled by the ratio of the number of the primary coils and secondary coil.
Types of Current in A Transformer
- The current in the primary circuit must be alternating current because alternating current can produce changing magnetic flux. A changing magnetic flux is needed to induce e.m.f. in the secondary coil.
- The induced current in secondary is also an alternating current. The frequency of the alternating current in the secondary coil is the same as the frequency of the primary current.
- The alternating in the secondary circuit can be converted into direct current by using a pair of diodes.
Symbol of A Transformer
 The figure on the left shows the symbol of a transformer. The 2 lines in between the coil denote the core.
The figure on the left shows the symbol of a transformer. The 2 lines in between the coil denote the core.